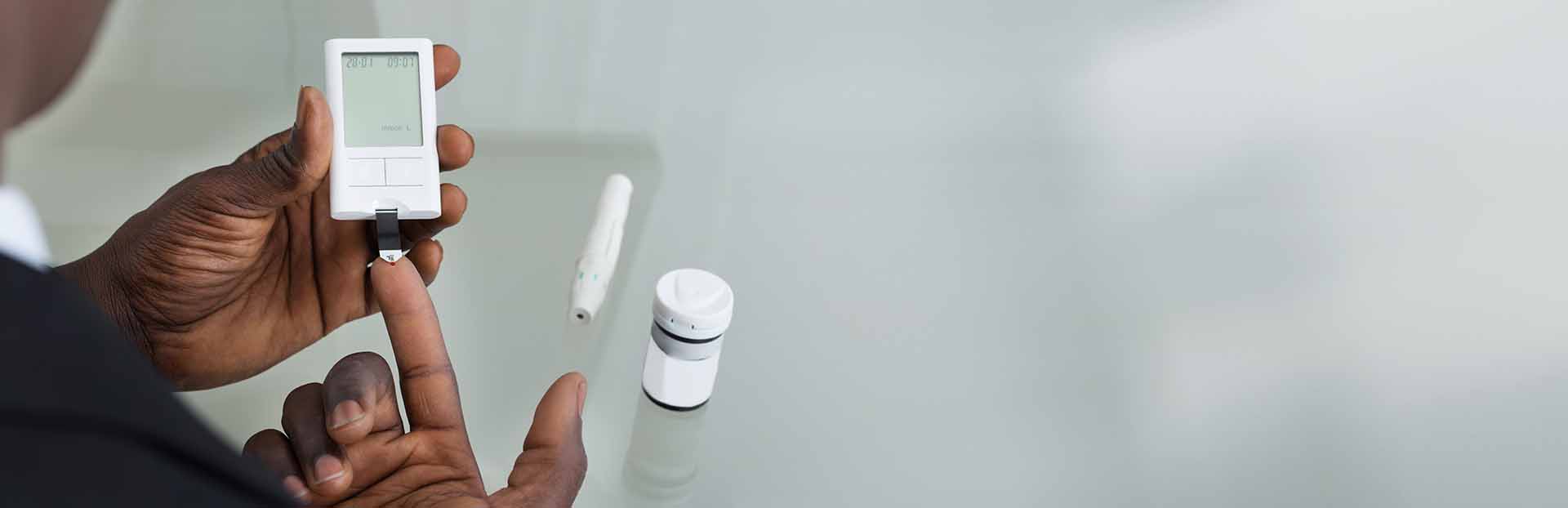

Ever wondered how much you know about Type 2 Diabetes? Its a common condition that affects many people. It's all about having too much glucose (sugar) in your blood for a long time. But don't worry, it can be managed with some lifestyle changes.
In Type 2 diabetes, your body doesn't use insulin properly, and sometimes your pancreas doesn't make enough of it. Insulin is like a helpful hormone that turns your food into energy and helps control your blood sugar levels. This type of diabetes is often connected to being overweight, not being active enough, using harmful stuff like tobacco or alcohol, or having a family history of diabetes.
Certain factors can increase your risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes, such as being over 45 years old, having high blood pressure, being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, or having had gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
To keep track of your blood sugar levels, there are certain ideal ranges to aim for, but don't worry if your numbers are a bit different as long as your doctor is okay with it. The ideal ranges are:

To manage Type 2 Diabetes, there's no cure, but you can lead a healthy lifestyle and take your medication as your doctor recommends. Here's what you can do:
If you're worried about low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), which can happen in Type 2 Diabetes, treat it quickly by eating or drinking something sugary, like sweets, non-diet sugary drinks, or fruit juice.

After your diagnosis, you'll have regular check-ups with your doctor to keep an eye on how you're doing and make sure your diabetes is under control. These check-ups include blood and urine tests to track your progress.
Remember, managing Type 2 Diabetes is all about making positive changes and staying on top of your health with the support of your doctor and care team.